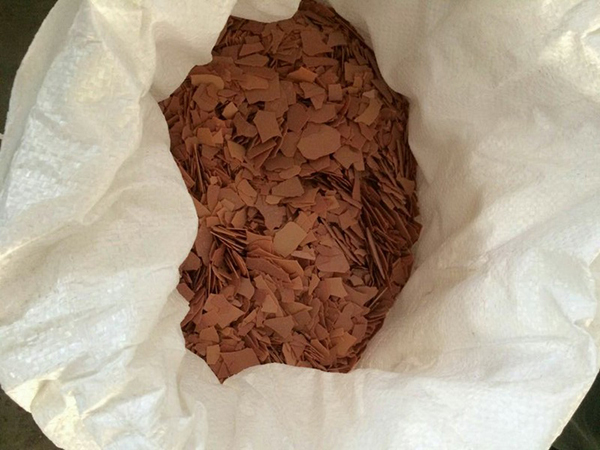

Sodium sulfide is also called stinky alkali, stinky soda, yellow alkali and sulfureted alkali. Sodium sulfide is a Inorganic compound, and pure Sodium sulfide is a colorless crystalline powder. Strong moisture absorption, easily soluble in water. The aqueous solution exhibits a strong alkaline reaction. Touching the skin and hair can cause burns. Therefore, Sodium sulfide is commonly known as alkali sulfide. Sodium sulfide aqueous solution will slowly oxidize into Sodium thiosulfate, Sodium sulfite, sodium sulfate and Sodium sulfide in air. As Sodium thiosulfate is generated rapidly, the main product of oxidation is Sodium thiosulfate. Sodium sulfide deliquests in the air, carbonates and deteriorates, constantly releasing hydrogen sulfide gas. Industrial Sodium sulfide is pink, brownish red and yellowish brown due to impurities. The specific gravity, melting point, and boiling point also vary due to the influence of impurities.
Chinese name: Sodium sulfide
English name: SODIUM SULFIDE
Alternative name: anhydrous Sodium sulfide, xanthine
Chemical formula: Na2S
Molecular weight: 78.04
CAS login number: 1313-82-2
EINECS login number: 215-211-5
Melting point: 950 ℃
Water solubility: 186 g/L (20 ℃)
Density: 1.86
physical property
At room temperature, pure products are colorless or slightly purple prismatic crystals, while industrial products often have pink, brownish red, or earthy yellow blocks due to impurities. Has a foul odor. Soluble in cold water, highly soluble in hot water, slightly soluble in alcohol. Industrial products are generally mixtures of Water of crystallization with different shapes, and contain impurities of different degrees. In addition to different appearance and color, density, melting point, boiling point, etc. are also different due to the influence of impurities.
chemical property
Decomposition in acid to produce hydrogen sulfide. Deliquescence occurs in the air while gradually undergoing oxidation, generating hydrogen sulfide when exposed to acid.
Explosive due to impact and high heat. When encountering acid, toxic hydrogen sulfide gas is produced, and anhydrous sulfide alkali has combustibility. Heating emits toxic sulfur oxide smoke.
Health hazard: This product can decompose into hydrogen sulfide in the gastrointestinal tract, which can cause hydrogen sulfide poisoning after oral administration. It has corrosive effects on the skin and eyes.
Hazard characteristics: Explosion can occur due to impact or rapid heating. Decomposes when exposed to acid, releasing highly toxic and flammable gases.
Combustion (decomposition) products: hydrogen sulfide, sulfur oxide.
Acute toxicity: LD50820mg/kg (oral administration in mice); 950mg/kg (intravenous injection to mice).
Related chemical reaction equation: 2Na+S=Na2S
application area
1. In the dye industry, it is used to produce Sulfur dye and is the raw material of sulfur blue and sulfur blue. The printing and dyeing industry is used as a dyeing aid for dissolving Sulfur dye. It is used in the leather industry to hydrolyze raw hides to remove hair, and also to prepare Sodium sulfide to accelerate the soaking and softening of dry hides. The papermaking industry is used as a cooking agent for paper. Textile manufacturing is a mordant used for denitration of man-made fibers, reduction of nitrified fabrics, and dyeing of cotton fabrics. The pharmaceutical industry is used to produce antipyretic drugs such as Phenacetin. In addition, it is also used to produce Sodium thiosulfate, Sodium hydrosulfide, Sodium sulfide, etc.
2. Adding an appropriate amount of Sodium sulfide to the alkaline etching solution of aluminum and alloy can significantly improve the quality of the etched surface, and can also be used to remove zinc and other alkali soluble heavy metal impurities in the alkaline etching solution.
3. Sodium sulfide can also be used for the treatment of conductive layer in direct electroplating. The purpose of forming a good conductive layer on the non-metallic surface is achieved through the reaction of Sodium sulfide and palladium to generate colloidal Palladium(II) sulfide.
4. Used as a corrosion inhibitor. It is also the raw material of Sodium thiosulfate, polynenenebb sodium sulfide, Sulfur dye, etc.
5. It is used to manufacture Sulfur dye, leather depilators, metal smelting, photography, rayon denitration, etc.
matters needing attention
Invasion pathway: inhalation and ingestion.
Respiratory system protection: Generally, no special protection is required, and if necessary, wear a gas mask.
Eye protection: Safety masks can be used.
Protective clothing: Wear anti-corrosion work clothes.
Hand protection: Wear rubber gloves.
Skin contact: Immediately rinse with water for at least 15 minutes. If there is a burn, seek medical treatment.
Eye contact: Immediately lift the eyelids and rinse with flowing water or physiological saline for at least 15 minutes, or rinse with 3% boric acid solution.
Inhalation: Remove from the site to a place with fresh air. Perform artificial respiration if necessary.
Ingestion: Those who take it by mistake should drink milk or egg white. Seek medical attention immediately.
Fire extinguishing method: Misty water, sandy soil.
Other: After work, take a shower and change clothes. Pay attention to personal cleanliness and hygiene.
Leakage emergency response:
Isolate the leakage pollution area and set Warning sign around it. Emergency response personnel shall wear Gas mask and chemical protective clothing. Do not come into direct contact with leaks. Avoid raising dust, collect with a clean shovel in a dry, clean, and covered container, and transport to a waste disposal site. You can also rinse with a large amount of water, and dilute the washing solution into the wastewater system. If there is a large amount of leakage, it should be collected and recycled or disposed of harmlessly before disposal.
Wastewater treatment method:
The wastewater that causes sulfide pollution is mainly alkaline wastewater, which can be neutralized. During the neutralization phase, a decrease in pH will result in some hydrogen sulfide escaping into the atmosphere, and utilizing the heat generated by the neutralization reaction will also increase the release rate of hydrogen sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide is released in large quantities in the air, which can pollute the air and disturb people. The Chloride process method can also eliminate sulfide pollution, which is also one of the effective methods, but it requires large amount of chlorine and costs high. In addition, iron or non-toxic iron salts (such as Iron(III) sulfate, Iron(III) chloride, etc.) are added to sulfide contaminated wastewater, and after 2-hour aeration, active Iron(III) oxide-hydroxide is produced, which can remove sulfide in the form of Iron(III) sulfide precipitation. Wastewater with serious sulfide pollution can also be neutralized by flue gas and then treated by Activated sludge.
Sulfides in water include soluble H2S, HS -, S2-, as well as soluble sulfides present in suspended solids, acid soluble metal sulfides, and non ionized inorganic and organic sulfides. Water containing sulfides often appears black and has a pungent odor, mainly due to the continuous release of H2S gas from the water. There are 8 in the air μ G/m3 of H2S can make people's sense of smell sensitive, and the threshold of H2S in water is 0.035 μ G/L. Sulfides in water are easily hydrolyzed and released into the air in the form of H2S. After being absorbed in large amounts, people immediately feel nauseous and vomiting, and may even experience breathing difficulties, suffocation, and a strong sense of toxicity. If the concentration reaches 15-30mg/m3 in the air, it can cause inflammation of the eye film and damage to the optic nerve. H2S, which escapes from the air and is inhaled by humans for a long time, can interact with the disulfide bonds (- S-S -) in cytochrome, oxidase, human protein, and amino acids, affecting the oxidation process of cells, causing cell hypoxia, and endangering human life. If water containing high levels of sulfides is consumed for a long time, it can cause dull taste, decreased appetite, weight loss, poor hair growth, and in severe cases, exhaustion and death.
Security Risk Security Terminology
S26: After accidental contact with eyes, please immediately rinse with plenty of water and seek medical advice. (In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with substance of water and seek medical advice.)
S45: If an accident or discomfort occurs, seek medical attention immediately (if possible, show its label). In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label when possible.)
S61: Avoid release to the environment. Refer to the special instructions/safety data sheet. (Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions/safety data sheets.)
Risk terminology
R31: Releases toxic gases when exposed to acid. (Contact with acids librates toxic gas.)
R34: Causes burns. (Causes burns.)
R50: Extremely toxic to aquatic organisms. (Very toxic to aquatic organisms.)